Flexible Sigmoidoscopy
Like colonoscopy, flexible sigmoidoscopy is an outpatient procedure used to diagnose and treat a number of problems encountered in the colon (large bowel). The main difference between the two procedures is that colonoscopy examines the entire colon whereas flexible sigmoidoscopy examines only the final portion of the colon that is joined to the rectum. This part of the colon is also known as the sigmoid colon and is located on the left side of the body, roughly between the bottom of the rib cage and the top of the hip bone.
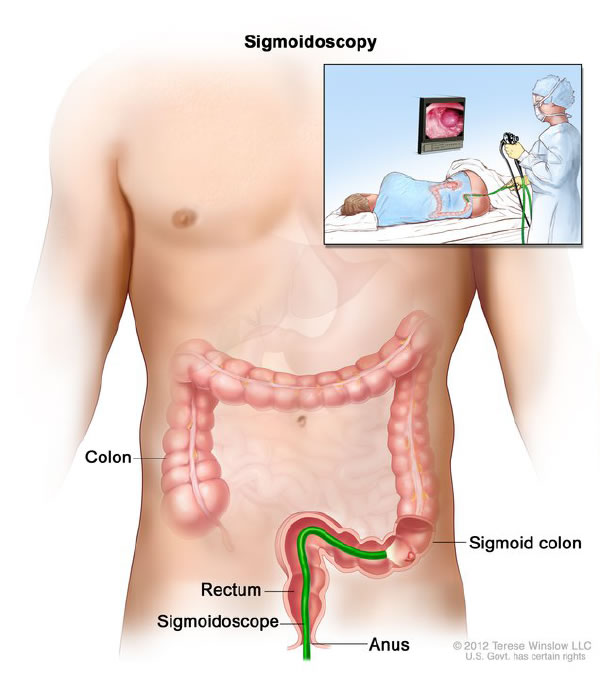
Flexible sigmoidoscopy is performed using a long, flexible hollow tube about the thickness of a finger, with a tiny video camera attached to the end. The scope is passed into your rectum and then moved slowly through the lower 40–50 cm of the colon, while images of its lining are taken by the camera and displayed on a television screen. These images are taken as the scope is being inserted and again as it is being withdrawn.
A good number of the conditions diagnosed and treated by a colorectal surgeon affect the rectum and sigmoid colon, so on many occasions it makes sense to look at this area first. If an abnormal area is seen, an instrument can be passed through the scope to take a small sample of tissue (biopsy) for examination in the laboratory. If no abnormality explaining your symptoms is found in this area of the colon, it may be necessary to proceed to examine the rest of the large bowel by colonoscopy.
Flexible sigmoidoscopy can also be used to remove polyps. Some polyps can become cancerous, so early detection and removal of these is important to protect against bowel cancer. If a polyp is seen during the procedure, a wire loop can be passed through the hollow scope and snare the base of the polyp, which is then severed from its attachment to the bowel wall by an electric current. Whilst I do not perform screening as part of our nationwide NHS bowel cancer screening programme, I do remove polyps up to a certain size if I see them while examining the bowel for another reason.
A flexible sigmoidoscopy usually takes about 10–20 minutes. You will be given an enema one hour prior to the procedure to empty your lower bowel. During the procedure, you will be required to lie on your left side with your knees drawn up. The procedure is not painful, so no sedation is required. However, to obtain clear views, a small amount of air is used to expand the colon and you may feel some mild cramping when air is introduced into the bowel. This cramping can be reduced by taking several slow, deep breaths during the procedure.
At the end of the procedure, the results will be discussed with you and any samples taken will be sent to the laboratory. A report is usually available shortly afterwards and a copy will be sent to your general practitioner. Providing you have not been sedated, you will be able to leave the clinic independently. Most people find that they can go about their normal daily activities when they leave the clinic.

